Year 7
Beginning Computer Science

This unit allows students to gain the skills and knowledge to use and access work on a computer system, communicate with emails and use word processors to present information well. Students will gain knowledge of how search engines work to improve the way they search for information.
Read MoreInside My Computer
This unit covers the key components inside a computer and explains how they work together. Students are introduced to representation and the binary number system that computers use to represent text in computers. Through this learning students gain a foundation of how hardware and software are used together.
Read MoreMy Personal eSafety

This unit teaches various dangers of using the Internet and the online world including, personal information on profiles, cyberbullying, digital footprints, fake news and screen time. Students will learn the dangers and the ways to minimise or remove threats from the online world. Furthermore, students learn additional digital literacy skills using office based presentation software and cover design based concepts to improve the look of publications.
Read MoreFlowcharts
This unit allows students to learn the main concepts used in computer programming which are essential to be able to select and use in problem solving. The unit gives students access to programming is a simplified and visual way that does not overload with both substantive and disciplinary knowledge commonly associated with learning to code. Students gain an insight into how programming controls devices and real world systems through the use of software mimic systems.
Read MorePRIMM Programming
This unit allows students to write programs that solve problems using block based code and deepens the knowledge of the key concepts of programming. The use of the PRIMM methodology supports students learning and scaffolds their progression in programming through developing code. The block based code allows students to have a visual representation of what their code will do and can easily recognise their practical work and success.
Read MoreMicro:bit Computing

This unit allows students to be independent with programming and problem solving in a new but familiar block-based programming environment. Students will branch out using literacy based problems cards to encourage reading and provide the tasks and support to problem solve and create useful programs for testing. Following research in gender imbalance for computer science, the use of physical computing devices helps to engage both girls and lower ability background students with programming and code rather than other programming experiences.
Read MoreYear 8
Binary Maths

This unit allows students to build on elements of both representation and programming. It also shows the links between the number systems and physical aspects of a computer through use of logic gates. Students explore representation further looking at key skills in conversion and addition. Furthermore, they will see the links between logic gates and expression seen in programming and how they use binary to control and create useful circuits in computers.
Read MorePaired Programming

This unit allows students to build on block based programming and knowledge of the concepts of programming from previous learning. Students will begin to learn text-based programming through the use of pairing; driver who codes and a navigator who problem solves, reads and debugs. Research-based practice shows that paired programming safely introduces text-based programming to students and raises success and engagement with the area of learning due to the safety net of working in pairs but swapping roles within lessons. Most programming is text-based with this unit preparing students for the approach and techniques needed to code without blocks.
Read MoreCyber Security

Students need to protect both themselves and the data and systems for their jobs or businesses. This unit allows them to learn the key aspects of malware threats, social engineering and the methods to prevent or protect with. Students showcase their learning through the development of a digital artefact (a poster) that has already been started and styled. They will refine both with information and the quality of that information; making better choices to find what is needed quickly, assess, select and format that information appropriately.
Read MoreHow My Computer Works

Students need to be able to understand how computer systems work as they expand into everyday life and the world of work in many different formats. The knowledge from this learning will develop students understanding of the key components inside a computer system and more importantly how they all work together to allow the computer to function. The final lesson introduces the basis of machine learning and AI which is at the forefront of current computing in the information age.
Read MoreDigital Graphics

Students need to be able to edit, combine and use graphical media to enhance their ability to communicate ideas either through that graphic or by using that as part of a bigger graphical product. The development of a digital graphic product will highlight the impact and influence of composition, colour and the use of text that when combined give the final product. Some of the substantial knowledge begins to introduce representation of images allowing students to understand how display screens work using pixels.
Read MoreYear 9
Augmented Reality
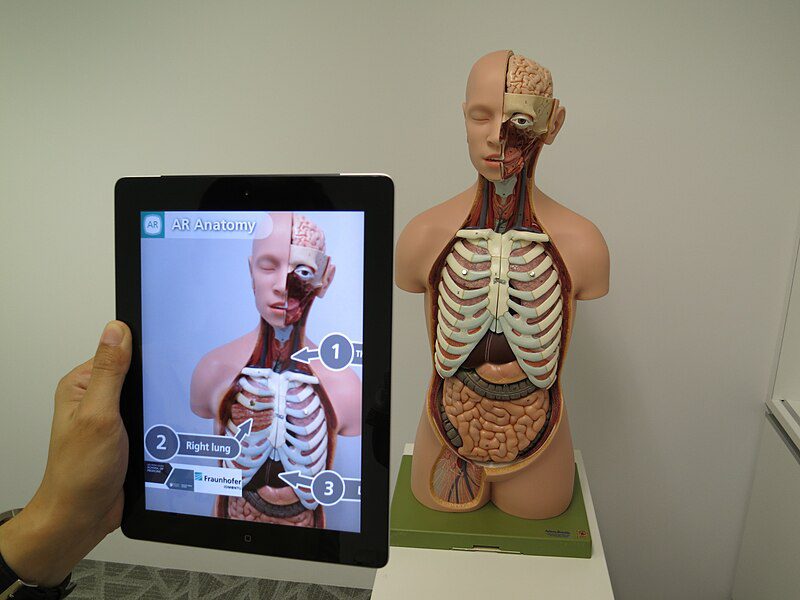
• Adobe Aero Systems
o Navigating a 3D workspace
o Importing Assets
o Layers
o Behaviours & Triggers
• Design Tools
o Mind Maps
o Flowcharts
• Creating an AR prototype for audience and purpose
Programming 3 (Text Based)

• Build upon skills developed in Unit 8.2 along with . . .
• Build and test programs using the selection & iteration constructs alongside lists/1D arrays
• Mathematical and relational operators
• Comparing algorithms
o Linear Search
o Binary Search
Spreadsheets
• Build upon skills developed in Unit 7.5 along with . . .
• Formulae & Functions (inc. the IF function)
• Formatting (inc. conditional formatting)
• Navigation between sheets
• Create a spreadsheet for audience and purpose
Data Representation
• Number Systems
o Binary & Denary
o Hexadecimal
• Data Representation
o Text (Character Sets)
o Bitmap Images
o Sounds
• Calculating File Sizes
The Connected World

• Wired & Wireless Networks
• LAN’s & WAN’s
• Network Hardware
• Methods of connectivity
o 4G / 5G
o Bluetooth
o Wi-Fi
Computational Thinking

Project based assignment based around the principles of:
o Audience & Purpose
o Use of a range of Software
o Design Tools
Mind Maps
Flowcharts
Visualisation Diagrams
o Computational Thinking
Abstraction
Decomposition
Algorithmic Thinking
Year 10
Memory and Storage
You will begin by learning some of the most important fundamentals of Computer Science, such as how data is stored and represented in different parts of the computer and for different types of data.
Read MoreProgramming Fundamentals

Programming Fundamentals builds on the introductory programming unit, first introduced in year 8. You will explore Programming constructs, in addition to several key Python functions. This unit will span the entire year, alongside the learning of theory topics.
Read MoreComputer Networks

You will learn the purpose of function of Computer Networks, from small LAN Networks to the largest Network we use - the Internet. This includes an understanding of the different hardware used and the functions of different topologies used today.
Read MoreSystem Architecture

In System Architecture you will look at the Fetch, Decode and Execute cycle and how this is applied within processors using Von Neumann Architecture. You will study the individual registers that make up a processor and how their individual roles support the processing of data and instructions.
Read MoreRobust Programming

This unit takes programming up a notch! You will learn how to anticipate misuse within your programs, and implement input validation and sanitisation in order to improve their reliablity. You will practice different methods of testing to ensure your programs are fully operational and are free of errors.
Read MoreNetwork Security

The Network Security unit teaches about the threats that are posed to computer systems and networks. You will then investigate ways to prevent attacks and mitigate damages received by systems.
Read MoreBoolean Logic
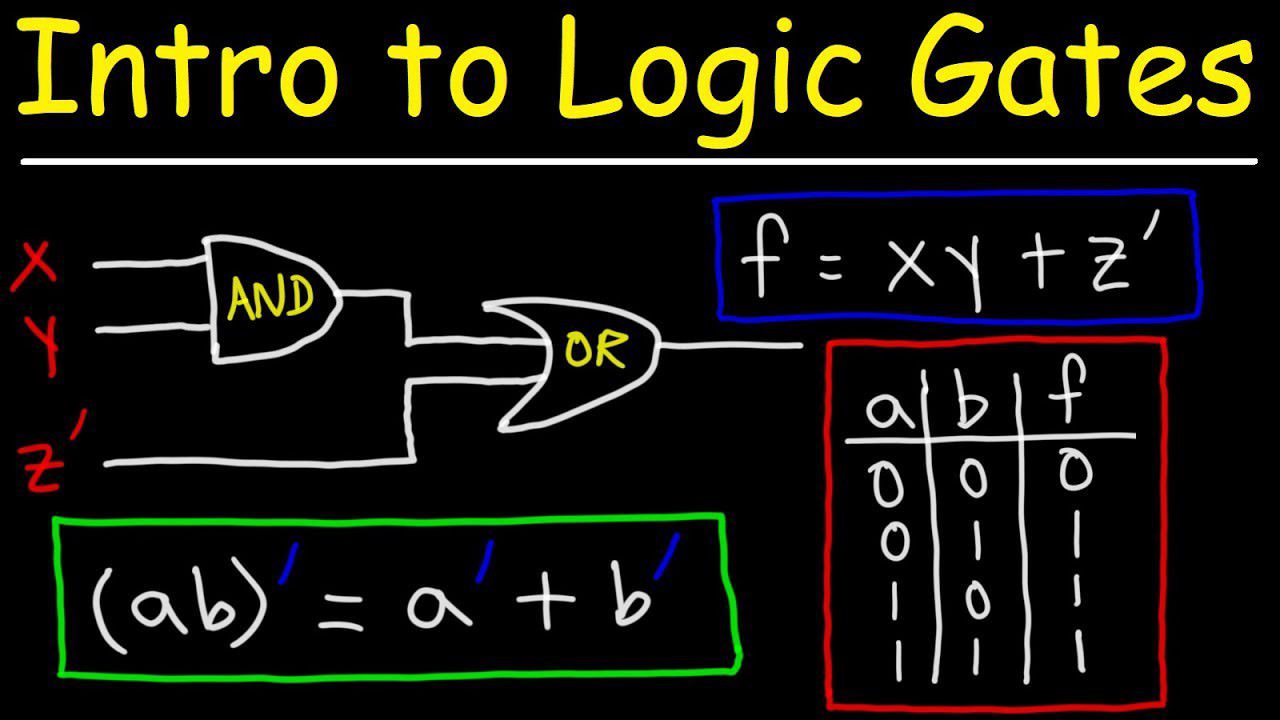
You will be introduced to several logic gates found inside computer systems. You will then investigate how logic is used within computers in order to solve problems through the use of logic diagrams and truth tables.
Read MoreAlgorithms
Reading, understanding and changing algorithms are an essential Computer Science skill. You will learn in this unit how to abstract key information out of problems, decompose problems into smaller sections and think "like a computer". You will learn to express algorithms in several ways such as, Flowcharts and Pseudocode.
Read MoreProgramming Project

You will undertake a substantial programming project in order to apply the programming skills you have learnt since Year 9. A set scenario will be given to you with a list of success criteria for you to achieve.
Read MoreYear 11
Network Protocols and layers

This unit investigates Computer Networks in more depth, this time looking at the different protocols (or rules) that are followed at different levels within the Network layers to enable error-free communication.
Read MoreProgramming Languages and IDEs

This unit explores the different generations of programming languages and the differences between them. It also teaches the different tools that are integrated within development environments in order to support programmers when creating code.
Read MoreProgramming Fundamentals

Programming Fundamentals builds on the introductory programming unit, first introduced in year 8. You will explore Programming constructs, in addition to several key Python functions. This unit will span the entire year, alongside the learning of theory topics.
Read MoreAlgorithms
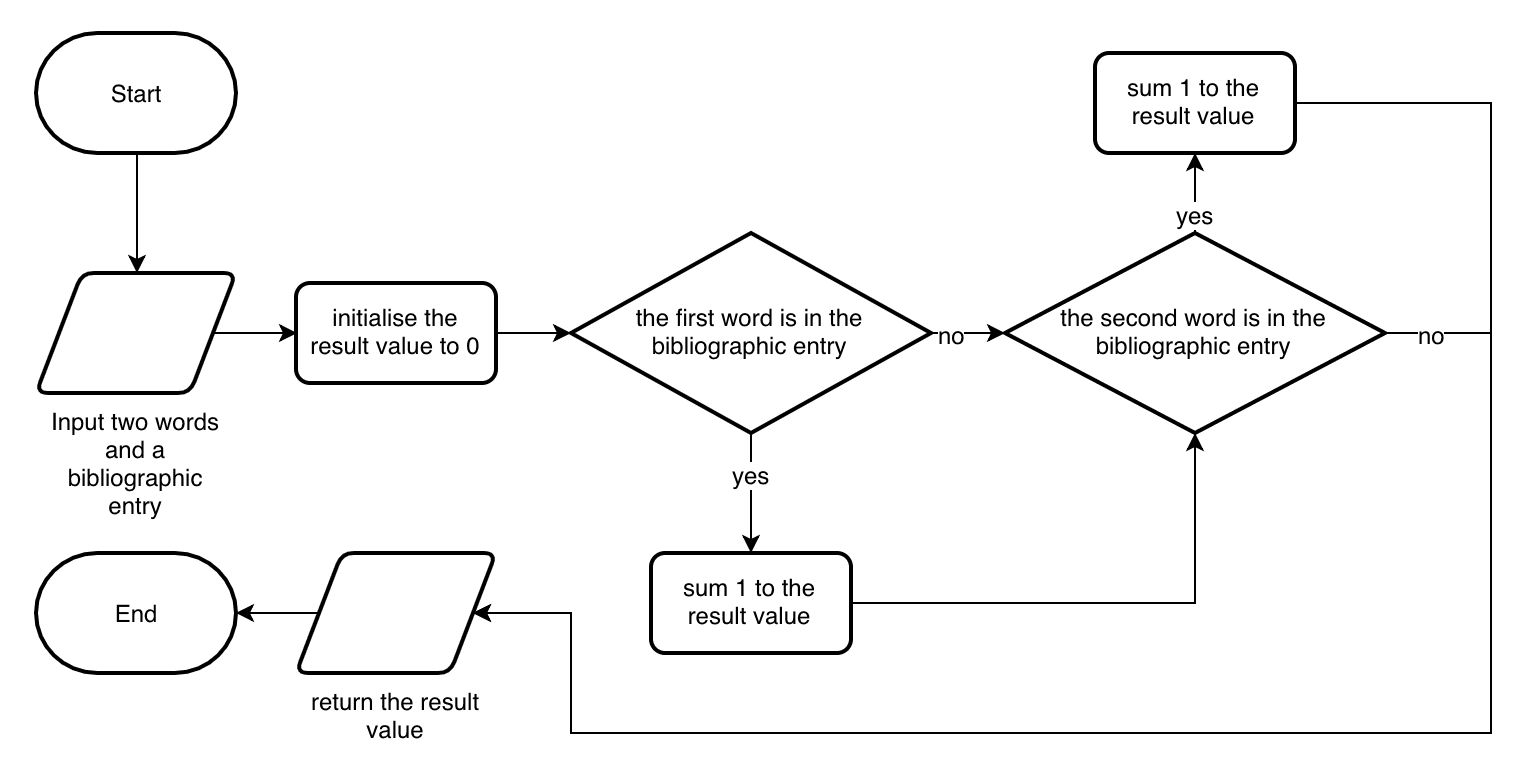
Reading, understanding and changing algorithms are an essential Computer Science skill. You will learn in this unit how to abstract key information out of problems, decompose problems into smaller sections and think "like a computer". You will learn to express algorithms in several ways such as, Flowcharts and Pseudocode.
Read MoreEthical, legal, cultural impacts

Within this unit you will learn how the developing use of technology can cause issues in the wider society. You will discuss Ethical, Legal, Cultural, Environmental and Privacy issues, and the laws that are associated with them.
Read More